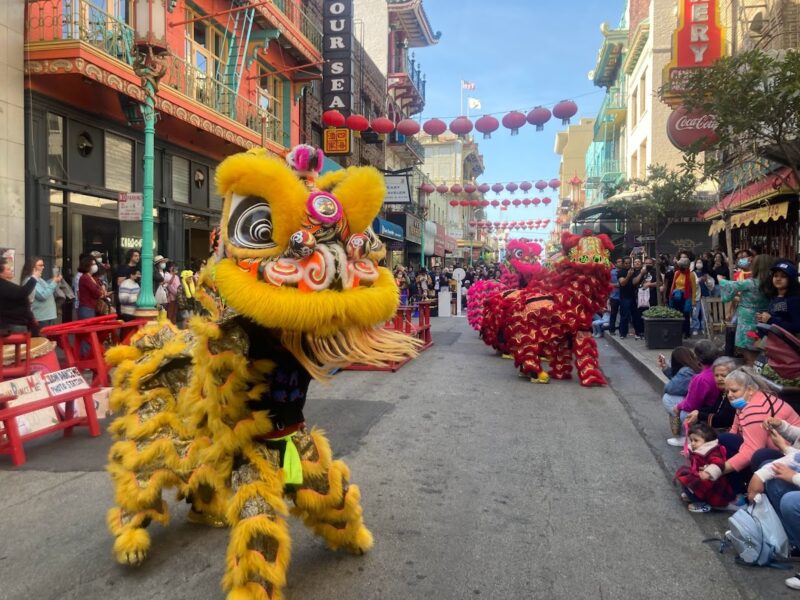
A dispute among Chinatown businesses appears to be temporarily quelled, following a decision by San Francisco’s Board of Appeals to limit amplified sound at outdoor events along a major tourist artery for the next two months.
Merchants had objected after a local dance company obtained the amplified-sound permit. It was the latest point of friction resulting from a gradual uptick in events, which have disrupted some businesses in the neighborhood.